Electromagnetic noise radiation is a term that might seem like it’s from a science fiction story. But it’s actually a real thing that affects our daily lives and technology. It’s present in the air we breathe and plays a role in our health. Understanding this concept can reveal how it impacts our world in unexpected ways.
Radiofrequency (RF) radiation is a type of electromagnetic noise that covers a wide range of frequencies, from 3 kHz to 300 GHz. It’s used in many technologies like wireless communication and medical devices. Knowing where it comes from, how it affects us, and its possible dangers is important for both advancing technology and keeping people safe.
The primary known effect of high-frequency electromagnetic radiation is thermal heating. At high levels, RF radiation can cause tissues to heat up, potentially leading to burns or other heat-related injuries. This principle is utilized in microwave ovens and certain medical therapies. However, typical environmental exposures, such as those from mobile phones and Wi-Fi routers, are generally well below the levels that cause significant heating.
In addition to thermal effects, researchers are investigating non-thermal effects of RF radiation. These effects occur at lower exposure levels where there is no noticeable heating. Studies have suggested that RF radiation might induce cellular stress responses, including the production of heat shock proteins and oxidative stress. These biological responses could potentially lead to longer-term health effects, though more research is needed to establish clear connections.
Sources of High-Frequency Electromagnetic Noise Radiation
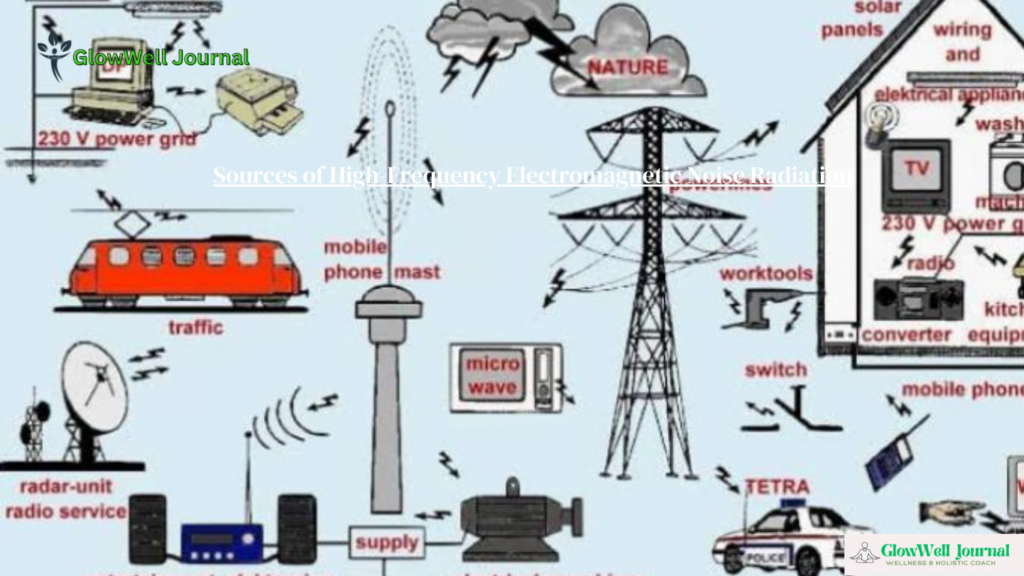
Communication Devices:
- Mobile Phones: Operate typically within the 800 MHz to 2.5 GHz range.
- Wi-Fi Routers: Commonly use frequencies around 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz.
- Bluetooth Devices: Operate around 2.4 GHz.
Broadcasting Systems:
- Radio and Television Transmitters: Use a range of frequencies for AM, FM, and digital broadcasts.
Industrial Equipment:
- Microwave Ovens: Operate at 2.45 GHz.
- Medical Devices: MRI machines and diathermy equipment use RF for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Environmental Sources:
- Solar Radiation: The sun emits electromagnetic radiation across a wide range of frequencies, including RF.
Effects of High-Frequency Electromagnetic Noise Radiation
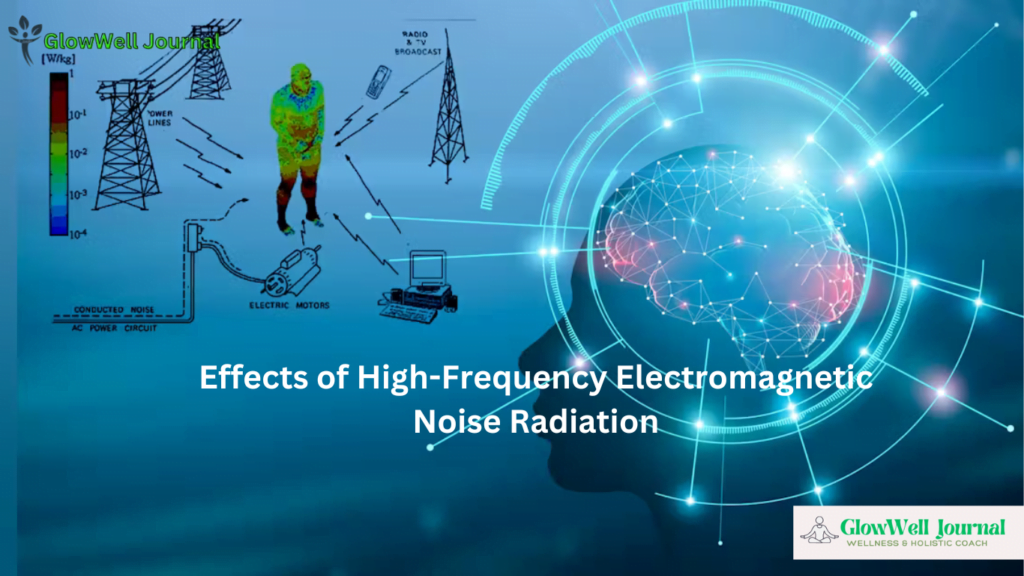
Interference with Electronics:
- High-frequency electromagnetic noise can interfere with the operation of electronic devices, leading to signal degradation, data loss, and operational malfunctions.
Biological Effects:
- Thermal Effects: One of the primary ways RF radiation affects the body is through thermal effects. High levels of RF exposure can cause tissue heating, which occurs when the energy from RF radiation is absorbed by body tissues. This can lead to:
Increased Body Temperature: Prolonged exposure to high levels of RF radiation can increase the temperature of body tissues, potentially causing heat-related injuries.
Localized Heating: Areas of the body that are closer to the RF source, such as the skin and eyes, can experience more significant heating.
- Non-Thermal Effects: Non-thermal effects are biological changes that occur at lower levels of RF exposure, where there is no significant heating of tissues. These effects are less well understood and are the subject of ongoing research. Some potential non-thermal effects include:·
Cellular Stress: RF radiation may induce stress responses in cells, leading to the production of heat shock proteins.
Oxidative Stress: There is evidence that RF radiation can increase the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cells, which can cause oxidative damage to cellular components.
Altered Cell Function: RF radiation may affect the function of cell membranes, potentially influencing ion channels and neurotransmitter release.
Human Health Issues and Effects on the Body
Cancer
One of the most significant concerns regarding RF radiation is its potential link to cancer. Some epidemiological studies have suggested a possible association between prolonged RF exposure and an increased risk of certain types of cancer, particularly brain tumors. The World Health Organization’s International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) has classified RF radiation as “possibly carcinogenic to humans” (Group 2B).
- Brain Tumors:Some studies have suggested a potential link between prolonged mobile phone use and an increased risk of gliomas and acoustic neuromas.
- Other Cancers: Research is ongoing to explore potential associations between RF radiation and other types of cancer, such as leukemia and breast cancer. However, findings are not yet conclusive.
Electromagnetic Hypersensitivity (EHS)
Electromagnetic hypersensitivity is a condition where individuals report experiencing symptoms such as headaches, fatigue, dizziness, and skin irritation in the presence of RF radiation. While the scientific community remains divided on whether EHS is caused directly by RF exposure or by psychological factors, it is recognized as a genuine health concern for those affected.
Reproductive Health
Some studies have indicated potential effects of RF radiation on reproductive health, including:
- Sperm Quality: Exposure to RF radiation from mobile phones has been linked to decreased sperm motility and viability in some studies.
- Developmental Effects: Concerns have been raised about the potential impact of RF radiation on fetal development, although more research is needed to draw definitive conclusions.
- Pregnancy and Fetal Development: Concerns have been raised about the potential impact of RF radiation on pregnancy outcomes and fetal development, though more research is needed for definitive conclusions.
Neurological and Cognitive Effects
Some research suggests that RF radiation exposure might affect brain function, potentially leading to changes in cognitive performance, memory, and attention. However, these findings are not consistently replicated across studies.
Cardiovascular Effects
There is limited evidence suggesting that RF radiation might influence heart rate variability and other cardiovascular parameters, but the clinical significance of these findings is still unclear.
Oxidative Stress and DNA Damage
RF radiation has been shown in some studies to increase the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can cause oxidative stress and potentially lead to DNA damage. The implications of these findings for long-term health are still under investigation.
Thermal Effects
High levels of RF exposure can cause tissue heating, which is the primary mechanism of injury in scenarios like exposure to microwave radiation. This can lead to burns and heat-related injuries in extreme cases.
Other Potential Effects
- Sleep Disturbances: Some studies suggest a link between RF radiation exposure and sleep problems, such as altered sleep patterns and decreased sleep quality.
- Immune System Effects: Limited evidence suggests that RF radiation might influence immune system function, but more research is needed to confirm these findings.
People Also Ask (PAA)
1. What are the main sources of high-frequency electromagnetic noise radiation in everyday life?
Ans: High-frequency electromagnetic noise radiation is primarily emitted by devices like mobile phones, Wi-Fi routers, Bluetooth gadgets, and microwave ovens. These sources are common in homes and workplaces, making RF radiation a part of our daily environment.
2. How can I reduce my exposure to high-frequency electromagnetic noise radiation?
Ans: You can reduce your exposure by using hands-free devices for phone calls, keeping your mobile phone away from your body when not in use, turning off Wi-Fi routers when not needed, and avoiding prolonged use of Bluetooth devices. Additionally, maintaining a distance from high-powered RF sources, like microwave ovens, can help minimize exposure.
3. Is it safe to sleep near a Wi-Fi router?
Ans: Sleeping near a Wi-Fi router might increase your exposure to RF radiation, but the levels are generally considered low and within safety guidelines. However, if you’re concerned, you can turn off the router at night or place it further away from your sleeping area.
4. Can RF radiation from mobile phones affect children differently than adults?
Ans: Children may be more susceptible to RF radiation due to their developing tissues and longer expected lifetime exposure. Some studies suggest potential risks, but more research is needed to fully understand the effects. It’s a good practice to limit children’s use of mobile phones and encourage the use of hands-free options.
5. What symptoms are associated with electromagnetic hypersensitivity (EHS)?
Ans: People with electromagnetic hypersensitivity (EHS) report symptoms such as headaches, fatigue, dizziness, skin irritation, and cognitive disturbances when exposed to electromagnetic fields, including RF radiation. The scientific basis for EHS is debated, but it remains a genuine concern for those affected.
6. Are there any long-term health risks associated with living near a cell tower?
Ans: Living near a cell tower may increase RF radiation exposure. While current evidence does not conclusively show long-term health risks, ongoing research is necessary to fully understand the potential impacts. Regulatory guidelines aim to keep exposure levels within safe limits.
7. How does RF radiation potentially impact male fertility?
Ans: Some studies have suggested that RF radiation from devices like mobile phones may reduce sperm motility and viability, potentially impacting male fertility. To mitigate risks, men can avoid keeping phones in their pockets for extended periods and use hands-free devices.
8. What precautions can pregnant women take to minimize RF radiation exposure?
Ans: Pregnant women can reduce RF radiation exposure by using hands-free devices, keeping mobile phones away from their abdomen, and limiting the use of wireless devices. Turning off Wi-Fi and Bluetooth when not in use can also help minimize exposure.
9. How do scientists study the health effects of RF radiation?
Ans: Scientists study the health effects of RF radiation through epidemiological studies, laboratory experiments, and clinical trials. They investigate potential links between RF exposure and various health outcomes, such as cancer, reproductive health issues, and neurological effects, to understand the underlying mechanisms and risks.
10. What are the current regulatory guidelines for safe RF radiation exposure?
Ans: Regulatory bodies like the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) and the International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP) set guidelines for safe RF radiation exposure levels. These guidelines are based on scientific research and aim to protect public health by limiting exposure to levels considered safe.
